
Principles by Ray Dalio
Rating: 10/10
Reading this book was a transformational experience. The book summarizes decades of distilled down wisdom from one of the world’s most successful business leaders. Ray started investing when he was 12 years old in the 1960s. At the time he invested his hard earned money delivering newspapers, mowing lawns, shoveling snow off driveways, washing dishes in a restaurant and caddying. He later founded Bridgewater Associates in 1975. The principles covered in the book are the basis for running Bridgewater and his life.
This post is just a snapshot of my key takeaways from the book. In the future, I plan to write a longer summary, and to start an evergreen note with my set of principles.
Memorable quotes
Life is like a game where you seek to overcome the obstacles that stand in the way of achieving your goals. You get better at this game through practice. The game consists of a series of choices that have consequences. You can't stop the problems and choices from coming at you, so it's better to learn how to deal with them. You have the freedom to make whatever choices you want, though it's best to be mindful of their consequences. The pain of problems is a call to find solutions rather than a reason for unhappiness and inaction, so it's silly, pointless, and harmful to be upset at the problems and choices that come at you (though it's understandable). We all evolve at different paces, and it's up to you to decide the pace at which you want to evolve. The process goes better if you are as accurate as possible in all respects, including assessing your strengths and weaknesses and adapting to them.
Management largely consists of scanning and probing everything for which you are responsible to identify suspicious signs. Based on what you see, you should vary your degree of digging, doing more of it for people and areas that look more suspicious, and less of it where probing instills you with confidence. With the right tools in place and performing well, your scanning will include both reviewing the output of these tools (e.g., "issues log", "metrics", "daily updates" and "checklists") and spot-checking.
Snapshot
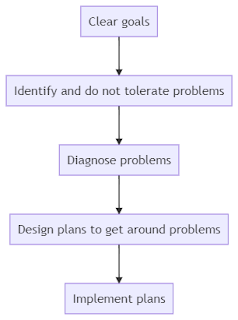
Know what you want. Make every effort possible to objectively understand reality (what is true). Do not tolerate problems that stand in the way of achieving your goals. Dig deep to understand the root cause, do not stop at the surface - people often confuse symptoms and root causes. Don't confuse problems with causes. "I can't get enough sleep" is not a problem; it is a cause of some problem. ... to avoid confusing the problem with its causes, try to identify the suboptimal outcome, e.g. "I am preforming badly in my job because I am tired." Develop plans to overcome these problems and diligently execute those plans.
Build teams and relationships in which people are prepared for radical transparency and ready to stay in sync. Triangulate your views with 2-3 other believable people to avoid missing important points or being mislead by your misjudgment.
Build a culture where it is ok to make mistakes, but it is absolutely unacceptable to not identify their root causes and identify / implement ways to avoid the same mistakes in the future.
Hiring people, assigning responsibilities, and keeping people honest about results are fundamental. The interview / evaluation process should not stop when you hire the person, but should continue indefinitely. Evaluate people accurately, not “kindly”. Sort people into other roles or fire them if they do not perform in their role well - and there isn't a realistic chance of improving their delivery with training and experience. People are different, some people can do a job well, others never will. A trick when hiring people: since everyone likes to select people similar to themselves, identify the traits you want to hire, look for a person on your team with those traits, ask the person to lead the selection process for you. Know your weaknesses and hire such that you bring in people that compensate for your weaknesses.
Build and manage a machine of process and people to achieve your goals. Continuously validate that your machine is delivering what is expected.
A good restaurateur constantly tastes the food that is coming out of his kitchen and judges it against his vision of what is excellent. A good manager needs to do the same.
Design the organization around goals, not tasks.
When facing problems, ask questions at two levels:
- What in the machine's design has led to this outcome? How should I alter the machine?
- What should I do in the current situation to overcome the immediate problem?
Ray Dalio's 210 Principles
- Trust in truth
- Realize you have nothing to fear from truth
- Create an environment in which everyone has the right to understand what makes sense and no one has the right to hold a critical opinion without speaking up about it
- Be extremely open – leads to truth and trust (don’t filter)
-
Have integrity and demand it from others
- Never say anything about a person you wouldn’t say to them directly and don’t try people without accusing them to their face
- Don’t let “loyalty” stand in the way of truth and openness
-
Be radically transparent
- Record almost all meeting and share them with all relevant people
-
Don’t tolerate dishonesty
- Don’t believe it when someone caught being dishonest says they have seen the light and will never do that sort of thing again
- Create a culture in which it is OK to make mistakes but unacceptable not to identify, analyze and learn from them
- Recognize that effective, innovative thinkers are going to make mistakes
- Do not feel bad about your mistakes or those of others. Love them!
- Observe the patterns of mistakes to see if they are a product of weaknesses
- Do not feel bad about your weaknesses or those of others
- Don’t worry about looking good – worry about achieving your goals. Most valuable comments are accurate criticisms
- Get over “blame” and “credit” and get on with “accurate” and “inaccurate”
- Don’t depersonalize mistakes. Identifying who made the mistake(s) is essential for learning
- Write down your weaknesses and the weaknesses of others to help remember and acknowledge them
- When you experience pain, remember to reflect. This is the ultimate time to test yourself to see if you can learn and grow from your pain
- Be self-reflective and make sure your people are self-reflective. When experiencing pain, don’t revert to fight or flight – reflect
-
Teach and reinforce the merits of mistake-based learning
- The most valuable tool we have for this is the issues log which is aimed at identifying and learning form mistakes
- Constantly get in Sync – constantly search for alternative viewpoints
- Constantly get in sync about what is true and what to do about it
- Talk about “is it true?” and “does it make sense?”
- Fight for right
-
Be assertive and open-minded at the same time
- Ask yourself whether you have earned the right to have an opinion
- Recognize that you always have the right to have and ask questions
- Distinguish open-minded people from closed-minded people
- Don’t have anything to do with closed-minded, inexperienced people
- Be wary of the arrogant intellectual who comments form the stands without having played on the field
- Watch out for people who think it’s embarrassing not to know
- Make sure responsible parties are open-minded about the questions and comments of others
-
Recognize that conflicts are essential for great relationships because they
are the means by which people determine whether their principles are aligned
and resolve their differences – don’t let the little issues slide as this
always results in a big blow up later
- Expect more open-minded disagreements at Bridgewater than at most other firms
- There is giant untapped potential in disagreement, especially if the disagreement is between two or more thoughtful people
-
Know when to stop debating and move on to agreeing about what should be done
– more important to do the big things well than the small things perfectly
- However, when people disagree on the importance of debating something, it should be debated
- Recgonize that “there are many good ways to skin a cat”
- For dissagreemtns to have a positive effect, people evaluating an individual decision or decision-maker must view the issue within a broader context
- Distinguish between idle complaints and complaints that are meant to lead to improvement
- Appreciate that open debate is not meant to create rule by referendum
-
Evaluate whether an issue calls for debate, discussion or teaching
- To avoid confusion, make clear which kind of conversation (debate, discussion or teaching) you are having
- Communication aimed at getting the best answer should involve the most relevant people
- Communication aimed at educating or boosting cohesion should involve a broader set of people than would be needed if the aim were just getting the best answer
- Leverage your communication (open e-mails to a FAQ board to be time efficient)
-
Don’t treat all opinions as equally valuable
- A hierarchy of merit is not only consistent with a meritocracy of ideas but essential for it
-
Consider your own and others’ “believabilities” – probability that a
person’s views will be right
- Ask yourself whether you have earned the right to have an opinion – it is much more difficult to have an opinion (a proper one at least) than most understand
- People who have repeatedly and successfully accomplished the thing in question and have great explanations when probed are most believable. The less of a track record someone has, the more questions they should have and the more experience the more assertive they should be
- If someone asks you a question, think first whether you’re the responsible party/right person to be answering the question
- Spend lavishly on the time and energy you devote to “getting in sync” because it’s the best investment you can make
-
If it is your meeting to run, manage the conversation
- Make it clear who the meeting is meant to serve and who is directing the meeting
- Make clear what type of communication you are going to have in light of the objectives and priorities – the worst people to choose to have in meetings with you are those who’s views align with yours
- Lead the discussion by being assertive and open-minded
- A small group (3 to 5) of smart, conceptual people seeking the right answers in an open-minded way will generally lead to the best answer
- 1+1 = 3 – two smart people working together are much more effective than if working alone
- Navigate the levels of the conversation clearly
- Watch out for “topic slip” – come to a conclusion on a topic before moving on
- Enforce the logic of conversations
- Worry about substance more than style
- Achieve completion in conversations – state the conclusion before moving on
- Have someone assigned to maintain notes in meetings and make sure follow-through happens
- Be careful not to lose personal responsibility via group decision making
- Make sure people don’t confuse their right to complain, give advice and debate with the right to make decisions
- Recognize that getting in sync is a two-way responsibility
- Escalate if you can’t get in sync
- Recognize the most important decisions you make are who you choose to be responsible party
- Remember that almost everything good comes from having great people operating in a great culture
-
First, match the person to the design
- Most importantly, find people who share your values – drive for excellence, truth at all costs, a high sense of ownership and a strong sense of character
- Look for people who are willing to look at themselves objectively and have character – what Ray respects most in people
- Conceptual thinking and common sense are required in order to assign someone the responsibility for achieving goals (as distinct form tasks)
- Recognize that the inevitable party is the person who bears the consequences of what is done
- By and large, you will get what you deserve over time
- The most important responsible parties are those who are most responsible for the goals, outcomes, and machines (they are those higher in the pyramid)
- Choose those who understand the difference between goals and tasks to run things
- Recognize that people are built very differently
- Think about their very different values, abilities and skills
- Understand that each person who works for you is like so that you know what to expect from them
- Recognize that the type of person you fit in the job must match the requirements for that job
- Use personality assessment tests and quality reflections on experiences to help you identify these differences
-
Understand that different ways of seeing and thinking make people suitable
for different jobs
- People are best at the jobs that require what they do well
- If you’re not naturally good at one type of thinking, it doesn’t mean you’re precluded from paths that require that type of thinking
- Don’t hide these differences. Explore them openly with the goal of figuring out how you and your people are built so you can put the right people in the right jobs and clearly assign responsibilities
- Remember that people who see things and think one way often have difficulty communicating and relating to people who see things and think another way
- Hire right, because the penalties of hiring wrong are huge
- Think through what values, abilities and skills you are looking for
- Weigh values and abilities more heavily than skills in deciding whom to hire
- Write the profile of the person you are looking for into the job description
-
Select the appropriate people and tests for assessing each of these
qualities and compare the results of those assessments to what you’ve
decided is needed for the job
- Remember that people tend to pick people like themselves, so pick interviewers who can identify what you are looking for
- Understand how to use and interpret personality tests
- Pay attention to people’s track records
- Dig deeply to discover why people did what they did – understanding the why helps you understand that person’s values
- Recognize that performance in school, while of some value in making assessments doesn’t tell you much about whether the person has the values and abilities you are looking for
- Ask for past reviews
- Check references
- Look for people who have lots of great questions
- Make sure candidates interview you and Bridgewater
- Don’t hire people just to fit the first job they will do at Bridgewater, hire people you want to share your life with
- Look for people who sparkle, not just “another one of those”
- Hear the click: find the right fit between the role and the person
- Pay for the person, not for the job
- Recognize that no matter how good you are at hiring, there is a high probability that the person you hire will not be the great person you need for the job
- Manage as someone who is designing and operating a machine to achieve the goal
-
Understand the difference between managing, micromanaging and not managing –
managing requires you to understand how well your people and designs are
working to achieve your goal and then refining this system
- Managing the people who report to you should feel like “skiing together”
- An excellent skier is probably going to be more critical and a better critic of another skier than a novice skier
- Constantly compare your outcomes to your goals
- Look down on your machine and yourself within it from the higher level – have the proper perspective
- Connect the case at hand to your principles for handling cases of that type
- Conduct the discussion at two levels when a problem occurs – the “machine” level discussion of why the machine produced that outcome and the “case at hand” discussion of what to do now about the problem
-
Don’t try to be followed; try to be understood and to understand others
- Don’t try to control people by giving them orders
- Communicate the logic and welcome feedback – explain the principles and logic behind decisions
- Clearly assign responsibilities – eliminate any confusion about expectations
-
Hold people accountable and appreciate them holding you accountable
- Distinguish between failures where someone broke their “contract” from ones where there was no contract to begin with
-
Avoid the “sucked down” phenomenon – when manager gets brought down to do
the tasks of a subordinate without acknowledging the problem
- Watch out for people who confuse goals and tasks because you can’t trust people with responsibilities if they don’t understand the goals
- Think like an owner, and expect the people you work with to do the same
-
Force yourself and the people who work for you to do difficult things
- Hold yourself and others accountable
- Don’t worry if your people like you; worry about whether you are helping your people and Bridgewater to be great
- Know what you want and stick to it if you believe it’s right, even if others want to take you in another direction
-
Communicate the plan clearly
- Have agreed-upon goals and tasks that everyone knows (from the people in the departments to the people outside the departments who oversee them)
- Watch out for the unfocused and unproductive “we should…(do something”
- Constantly get in sync with your people
- Get a “threshold level of understanding”
-
Avoid staying too distant
- Tool – use daily updates as a tool for staying on top of what your people are doing and thinking
- Learn confidence in your people – don’t presume it
- Vary your involvement based on your confidence
- Avoid the “theoretical should”
- Care about the people who work for you
- Logic, reason and common sense must trump everything else in decision making
- While logic drives our decisions, feelings are very relevant
-
escalate when you can’t adequately handle your responsibilities, and make
sure that the people who work for you do the same
- Make sure your people know to be proactive
- Tool – an escalation button
- Involve the person who is the point of the pyramid when encountering material cross-departmental or cross sub-departmental issues
- Probe deep and hard to learn what to expect from your “machine”
- Know what your people are like and make sure they do their jobs excellently
-
Constantly probe the people who report to you and encourage them to probe
you
- Remind the people you are probing that problems and mistakes are fuel for improvement
- Probe the level below the people who work for you
- Remember that few people see themselves objectively, so it’s important to welcome probing and to probe others
-
Probe so that you have a good enough understanding of whether problems are
likely to occur before they actually do
- When a crisis appears to be brewing, contact should be so close that it’s extremely unlikely that there will be any surprises
- Investigate and let people know you are going to investigate so there are no surprises and they don’t take it personally
- Don’t “pick your battles.” Fight them all
- Don’t let people off the hook
- Don’t assume that people’s answers are correct
- Make the probing transparent rather than private
- Evaluate people accurately, not “kindly”
-
Make accurate assessments
- Use evaluation tools such as performance surveys, metrics and formal reviews to document all aspects of a person’s performance. These will help clarify assessments and communication surrounding them
- Maintain “baseball cards” and/or “believability matrixes” for your people – ratings, rankings, credentials, track record
- Evaluate employees with the same rigor as your evaluate job candidates
- Know what makes your people tick, because people are your most important resource
- Recognize that while most people prefer compliments over criticism, there is nothing more valuable than accurate criticisms
- Make this discovery process open, evolutionary and iterative
-
Provide constant, clear and honest feedback and encourage discussion of this
feedback
- Put your compliments and criticisms into perspective
- Remember that convincing people of their strengths is generally much easier than convincing them of their weaknesses
- Encourage objective reflection – lots and lots of it
- Employee reviews – the goal of a review is to be clear about what the person can and cannot be trusted with and from there “what can I do about it” can be assessed
- Understand that you and the people you manage will go through a process of personal evolution
- Recognize that your evolution should be relatively rapid and a natural consequence of discovering your strengths and weaknesses; as a result, your career path is not planned at the outset
-
Remember that the only purpose of looking at what people did is to learn
what they are like
- Look at patterns of behaviors and don’t read too much into any one event
- Don’t believe that being good or bad at some things means that the person is good or bad at everything
- If someone is doing their job poorly, consider whether this is due to inadequate learning (training/experience) or inadequate ability
-
Remember that when it comes to assessing people, the two biggest mistakes
are being overconfident in your assessment and failing to get in sync on
that assessment. Don’t make those mistakes
- Get in sync in a non-hierarchical way regarding assessments
- Learn about your people and have them learn about you with very frank conversations about their mistakes and their root causes
- Help people through the pain that comes with exploring their weaknesses
- Recognize that when you are really in sync with people about weaknesses, whether yours or theirs, they are probably true
- Remember that you don’t need to get to the point of “beyond a shadow of a doubt” when judging people
- Understand that you should be able to learn the most about what a person is like and whether they are a “click” for the job in their first year
- Continue assessing people throughout their time at Bridgewater
- Train and test people through experiences
- Understand that training is really guiding the process of personal evolution
- Know that experience creates internalization
- Provide constant feedback to put the learning in perspective
- Remember that everything is a case study
- Teach your people to fish rather than give them fish
-
Recognize that sometimes it is better to let people make mistakes so that
they can learn from them rather than tell them the better decision
- When criticizing, try to make helpful suggestions
- Learn from success as well as from failure – point out people who are performing a job well so there is a role model to replicate
- Know what types of mistakes are acceptable and unacceptable, and don’t allow the people who work for you to make the unacceptable ones
- Recognize that behavior modification typically takes about 18 months of constant reinforcement
-
Train people; don’t rehabilitate them
- A common mistake – training and testing a poor performer to see if he/she can acquire the required skills without simultaneously trying to assess their abilities
- After you decide “what’s true” (after you figure out what your people are like), think carefully about “what to do about it”
- Sort people into other jobs at Bridgewater, or remove them from Bridgewater
- When you find that someone is not a good “click” for a job, get them out of it ASAP
- Know that it is much worse to keep someone in a job who is not suited for it than it is to fire someone
- When people are “without a box,” consider whether there is an open box at Bridgewater that would be a better fit. If not, fire them
- Do not lower the bar
- Know how to perceive problems effectively
- Keep in mind the 5-step process explained in Part 2
- Recognize that perceiving the problems is the first essential step toward great management
- Understand that problems are the fuel for improvement
- You need to be able to perceive if things are above the bar (good enough) or below the bar (not good enough) and you need to make sure your people can as well
- Don’t tolerate badness
- “Taste the soup” – try out your product often and analyze it against your vision of what excellent should be
-
Have as many eyes looking for problems as possible
- “Pop the cork”
- Hold people accountable for raising their complaints
- The people closest to certain jobs probably know them best, or at least have perspectives you need to understand, so those people are essential for creating improvement
- To perceive problems, compare how the movie is unfolding relative to your script
- Don’t use the acronyms “we” and “they,” because that masks personal responsibility – use specific names
- Be veyr specific about problems; don’t start with generalizations
- Tool – use the following tools to catch problems – issue logs, metrics, surveys, checklists, outside consultants and inside auditors
- The most common reason problems aren’t perceived is what I call the “frog in the boiling water” problem – there is a strong tendency to get used to very bad things which would be shocking of seen with fresh eyes
-
In some cases, people accept unacceptable problems because they are
perceived as being too difficult to fix. Yet fixing unacceptable problems is
actually a lot easier than not fixing them, because not fixing them will
make you miserable
- Problems that have good, planned solutions are completely different from those that don’t
- Diagnose to understand what the problems are symptomatic of
- Recognize that all problems are just manifestations of their root causes, so diagnose to understand what the problems are symptomatic of
- Understand that diagnosis is foundational both to progress and quality relationships
-
Ask the following questions when diagnosing:
- Ask what sub optimally did you experience?
- Is there a clear responsible party for the suboptimality?
- Ask responsible party what the “mental map” was supposed to work
- Ask what, if anything, broke the situation
- Ask why they handled the problem the way they did (root cause is not action or a reaction – it is a reason
- Is this consistent with prior patterns?
- Remember that a root cause is not an action but a reason
- Identify which step failure occurred in the 5-step process
- Remember that a proper diagnoses requires a quality, collaborative and honest discussion to get at the truth
- Keep in mind that diagnoses should produce outcomes
- Don’t make too much out of one “dot” – synthesize a richer picture by squeezing lots of “dots” quickly and triangulating with others
- Maintain an emerging synthesis by diagnosing continuously
- To distinguish between a capacity issue and a capability issue, imagine how the person would perform at that particular function if they had ample capacity
- The most common reasons managers fail to produce excellent results or escalate are they are too far removed, have problems discerning quality differences, have lost sight of how bad things have become, too much pride to admit poor work, fear adverse consequences from admitting failure
- Avoid “Monday morning quarterbacking” – hindsight is always 20/20 – imagine what could have reasonably been known when the decision was made
- Identify the principles that were violated
- Remember that if you have the same people doing the same things, you should expect the same results
- Use the following “drilldown” technique to gain an 80/20 understanding of a department or sub-department that is having problems – list problems and causes/diagnoses, design a plan, execute, monitor and modify the plan. People perform poorly either because of insufficient training or insufficient ability. Your job as a manager to get at truth and excellence, not to make people happy
- Put things in perspective
-
Go back before going forward
- Tool – have all new employees listen to tapes of “the story” to bring them up to date
- Understand “above the line” and “below the line” thinking and how to navigate between the two
- Design your machine to achieve your goals
-
Remember, you are designing a “machine” or system that will produce outcomes
- A short-term goal probably won’t require you to build a machine
- Beware of paying too much attention to what is coming at you and not enough attention to what your responsibilities are or how your machine should work to achieve your goals
- Don’t act before thinking. Take the time to come up with a game plan
- The organizational design you draw up should minimize problems and maximize capitalization opportunities
- Put yourself in the “position of pain” for a while so that you gain a richer understanding of what you’re designing for
- Recognize that design is an interative process; between a bad “now” and a good “then” is a “working through it” period
- Visualize alternative machines and their outcomes, and then choose
- Think about second and third-order consequences as well as first-order consequences
-
Most importantly, build the organization around goals rather than tasks
- First come up with the best workflow design, sketch it out in an organizational chart, visualize how the parts interact, specify what qualities are required for each job, and , only after that is done, choose the right people to fill the jobs
- Organize departments and sub-departments around the most logical groupings
- Make departments as self-sufficient as possible so that they have control over the resources they need to achieve the goals
- The efficiency of an organization decreases and the bureaucracy increases in direct relation to the increase in the number of people and/or the complexity of the organization
-
Build your organization from the top down
- Everyone must be overseen by a believable person who has high standards
- The people at the top of each pyramid should have the skills and focus to manage their direct reports and a deep understanding of their jobs
- The ratio of senior managers to junior managers and to the number of people who work two levels below should be limited, to preserve quality communication and mutual understanding
- The number of layers from top to bottom and the ratio of managers to their direct reports will limit the size of an effective organization (about 5 to 1)
- The larger the organization, the more important are the information technology expertise in management and cross-departmental communication
- Do not build the organization to fit the people
-
Have the clearest possible delineation of responsibilities and reporting
lines
- Create an organizational chart to look like a pyramid, with straight lines down that don’t cross
-
Constantly think about how to produce leverage
- You should be able to delegate the details away- if not your employees are either badly trained or they are the wrong people – manager should only have to worry about things going smoothly
- It is far better to find a few smart people and give them the best technology than to have a greater number of ordinary and less well-equipped people
- Use “leveragers”
- Understand the clover-leaf design – 2 to 3 responsible parties who are willing to challenge and check each other (more likely to fight for what they believe in and sorting out issues earlier than they otherwise would be)
- Don’t do work for people in another department or grab people from another department to do work for you unless you speak to the boss
- Watch out for “department slip”
- Assign responsibilities based on workflow design and people’s abilities, not job titles
- Watch out for consultant addiction
- Tool – maintain a procedure manual
-
Tool – use checklists
- Don’t confuse checklists with personal responsibility
- Remember that “systematic” doesn’t necessarily mean computerized
- Use “double-do” rather than “double-check” to make sure mission-critical tasks are done correctly
- Watch out for “job slip”
- Think clearly how things should go and when they aren’t going that way, acknowledge it and investigate
-
Have good controls so that you are not exposed to the dishonesty of others
and trust is never an issue
- People doing auditing should report to people outside the department being audited, and auditing procedures should not be made known to those being audited
- Remember there is no sense in having laws unless you have policemen (auditors)
- Do what you set out to do
- Push through! – you must MAKE great things happen
- Recognize the power of knowing how to deal with not knowing
- Recognize that your goal is to come up with the best answer, that the probability of your having it is small, and that even if you have it, you can’t be confident that you do have it unless you have other believable people test you
-
Understand that the ability to deal with not knowing is far more powerful
than knowing
- Embrace the power of asking “What don’t I know, and what should I do about it?”
- Finding the path to success is at least as dependent on coming up with the right questions as coming up with answers
- Remember that your goal is to find the best answer, not to give the best one you have
- While everyone has the right to have questions and theories, only believable people have the right to have opinions
-
Constantly worry about what you are missing
- Successful people ask for the criticism of others and consider its merit
- Triangulate your view – never make important decisions without asking at least 3 believable people and ask them to probe your own reasoning
- Make all decisions logically, as expected value calculations
-
Considering both the probabilities and the payoffs of the consequences, make
sure that the probability of the unacceptable (the risk of ruin) is nil
- The cost of a bad decision is equal to or greater than the reward of a good decision, so knowing what you don’t know is at least as valuable as knowing
- Recognize opportunities where there isn’t much to lose and a lot to gain, even if the probability of the gain happening is low
- Understand how valuable it is to raise the probability that your decision will be right by accurately assessing the probability of your being right
- Don’t bet too much on anything. Make 15 or more good, uncorrelated bets
- Remember the 80/20 Rule, and know what the key 20% is
-
Distinguish the important things from the unimportant things and deal with
the important things first
- Don’t be a perfectionist
- Since 80% of the juice can be gotten with the first 20% of the squeezing, there are relatively few (typically less than five) important things to consider in making a decision
- Watch out for “detail anxiety”
- Don’t mistake small things for unimportant things, because some small things can be very important
- Think about the appropriate time to make a decision in light of the marginal gains made by acquiring additional information versus the marginal costs of postponing the decision
- Make sure all the “must do’s” are above the bar before you do anything else
- Remember that the best choices are the ones with more pros than cons, not those that don’t have any cons. Watch out for people who tend to argue against something because they can find something wrong with it without properly weighing all the pros against the cons
- Watch out for unproductively identifying possibilities without assigning them probabilities, because it screws up prioritization
-
Understand the concept and use the phrase “by and large”
- When you ask someone whether something is true and they tell you that “it’s not totally true,” it’s probably true enough
- Synthesize
- Understand and connect the dots
- Understand what an acceptable rate of improvement is, and that it is the level and not the rate of change that matters most
- If your best solution isn’t good enough, think harder or escalate that you can’t produce a solution that is good enough
- Avoid the temptation to compromise on that which is uncompromisable
- Don’t try to please everyone

Comments
Post a Comment